How to Know if You Have an Abscessed Tooth

Tooth abscesses can be painful, but they are treatable and can be taken care of quickly by a good endodontist. You should visit the dentist right away when you experience the symptoms of an abscessed tooth, as it can cause serious complications if left untreated.
What Is an Abscessed Tooth?
An abscessed tooth is a bacterial infection that creates pus inside the tooth. It often forms in the root, which is referred to as a periapical abscess. Symptoms of an abscessed tooth include:
- Sensitivity to hot and cold.
- Pain with chewing or biting.
- Facial swelling.
- Tender lymph nodes beneath the jaw.
- A severe toothache that you feel throughout your jawbone.
- A fever.
Are There Different Kinds of Tooth Abscesses?
A tooth abscess is defined by the location or region where it forms in the tooth. The three major types of tooth abscesses are:
1. Gingival Abscess
Also called a gum abscess, a gingival abscess is a lesion that forms between your gum and tooth. It is usually visible along the gumline and grows quickly.
Gingival abscesses are typically painful when the bacteria infect the gum area. Although this type of abscess can result from poor oral hygiene, it is commonly caused by a foreign object entering your gum. Your dentist can remove the food particle, splinter or other trapped object and give you an antibiotic.
2. Periodontal Abscess
A periodontal abscess creates pus inside the gum tissue, resulting in a shiny, swollen area that is usually sensitive to changes in pressure. Your tooth near the abscess may feel loose.
This type of abscess is common in patients with periodontal disease. Consistently poor oral hygiene can lead to a build-up of tartar — hardened dental plaque — and gum disease, eventually resulting in bone loss if left untreated.
3. Periapical Abscess
A periapical abscess causes pus from a bacterial infection to form in the tooth’s root. Bacteria can enter the pulp through a cavity or an injury to the tooth’s surface, like a crack.
The dental pulp is where the tooth is innervated. This type of abscess can cause inflammation and swelling. The tooth will feel painful as the abscess forms, but if left to progress, the tooth may eventually go numb.
What Does a Tooth Abscess Look and Feel Like?
You might be asking yourself, “What’s an abscessed tooth feel like?” An abscess feels painful and tender. The buildup of pus generally occurs at the bottom of the root and looks like pus buildup in any other part of the body, containing yellow, foul-smelling liquid. A tooth abscess puts pressure on the rest of the tooth and makes everything feel sensitive and even hot to the touch. Tooth abscess stages include:
- Dental decay, which impacts the dentin and enamel of the tooth.
- An extension of the decay into the nerve and pulp.
- A buildup of the infection in the root, which can spread to bones, gums and other teeth if you do not seek treatment.
Can You Have an Abscessed Tooth Without Pain?
Occasionally, people feel no pain when they have a tooth abscess. A painless abscess will normally have other symptoms, like swelling in your gums and cheeks. It is rare to have an entirely pain-free tooth abscess, which may present as a bubble on your gum.
Reasons your abscessed tooth could be painless include:
- A previous root canal: If the abscessed tooth needed a root canal treatment in the past, the dead nerve connected to the tooth is unable to transfer pain signals to your brain.
- Dead inner tissue: When bacteria leak into the inner chamber of your tooth, the resulting infection can attack the nerve in the tooth’s inner tissue. This leads to tissue death and prevents the nerve from functioning.
- An active immune system: If your immune system launches an attack against the infection inside your tooth, the abscess could be painless.
If you notice any potential symptoms of a tooth abscess, make sure you visit your dentist so they can take x-rays of your mouth. If you experience a mouth injury, seek treatment right away.
Causes of Tooth Abscesses
Tooth abscesses are caused by bacteria attacking the dental pulp, which includes nerves and blood vessels. Bacteria may invade the tooth through a chip, crack or cavity and travel into the root. You are more likely to experience a tooth abscess if you:
- Practice poor dental hygiene: Not brushing or flossing your teeth regularly increases the likelihood of developing tooth decay and gum disease, which can lead to abscesses.
- Experience dry mouth: Saliva moves bacteria out of the mouth, and a lack of saliva can boost the risk of tooth decay. Aging or side effects of some medications may cause dry mouth.
- Consume a poor diet: Eating a lot of sugary foods like sweets can cause tooth decay and lead to cavities that turn into tooth abscesses.
- Avoid or delay dental checkups: If you avoid regular teeth cleanings and dental exams, you are at an increased risk for developing a tooth abscess. Delaying treatment when you have a sore tooth could lead to worsening dental health.
- Practice a contact sport without proper equipment: A loose or cracked tooth could lead to a tooth abscess. Always wear a mouth guard if you participate in an active contact sport.
Tooth Abscess Stages
A tooth abscess begins with untreated tooth decay that has progressed into an infection of the inner tooth. The tooth abscess stages are:
1. Tooth Decay
The first stage of a tooth abscess is gradually advancing tooth decay. When caught in the early stages, tooth decay is easier to treat. If left untreated, tooth decay progresses in this order:
- Enamel: Erosion of the outer coating of your tooth (enamel) is usually caused by excess plaque buildup on your teeth. This stage may present as tooth sensitivity, but it is often asymptomatic. You may notice white spots on the surface of your tooth.
- Dentin: Tooth decay can seep beneath your enamel, damaging the dentin layer. You may have tooth sensitivity or a sharp pain in your tooth that you can feel when you drink something cold. You may see a hole in your tooth.
- Pulp: The soft inner layer of your tooth is called the pulp. When tooth decay reaches the nerve inside the pulp, an abscess starts to form, and you could initially experience severe pain or pulpitis. Your tooth pain may gradually fade if you continue to go without treatment.
2. Abscess Formation
As tooth decay progresses into the pulp, bacteria attack the nerve, and an abscess forms. You may notice a bump on your gumline, inflammation inside your mouth and gum swelling. You may also experience throbbing pain in your gums or teeth. If your infection is severe, you might also have a fever and chills. The bacteria can spread into your jawbone in this stage.
3. Complications
Once you have a tooth abscess, you are highly likely to experience serious complications if you continue to avoid treatment. These complications include:
- Tooth loss: Tooth decay that has progressed into an abscess can cause the tooth to break or fall out.
- Sepsis: This is a rare but life-threatening infection caused by the bacteria from your abscessed tooth spreading into your bloodstream.
What to Do if You Have Sepsis From a Tooth Abscess
Sepsis is a very rare complication that can be related to other types of infections. If you have an abscessed tooth, and you think you might have developed sepsis, stay calm and go to the nearest emergency room.
If you have sepsis, in addition to tooth pain and other symptoms of an abscess, you may experience:
- Facial swelling of the cheeks or around the mouth
- Swelling around the gums
- A high fever
- Chills
- Sweating
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Fatigue
- Mental confusion
Things to Avoid if You Have a Dental Abscess
If you suspect that you have a dental abscess, it’s important to seek treatment right away. Even if your tooth pain or sensitivity turns out to be a less serious condition, it’s important to get the dental care you need.
If you are experiencing symptoms that could be related to a dental abscess, here are some things to avoid:
- Delaying treatment: You might feel nervous about going to an appointment or think you have too little time to go until a certain date. Get in to see your dentist as soon as possible.
- Halting your dental hygiene routine: Even if your teeth and gums hurt or feel sensitive, continue to brush and floss as a regular routine. You may need to purchase a soft toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums.
- Chewing on the sore side of your mouth: Try to chew on the other side of your mouth until you are able to see your dentist.
- Popping or rupturing a visible abscess: A ruptured abscess can spread bacteria to other parts of your mouth. It will also open the area to more bacteria.
- Mistaking a lack of pain for healing: You can have a painless abscess, or an abscess can start out as feeling painful but gradually go numb. If your tooth stops hurting, you still need to see your dentist if you have been experiencing other symptoms.
Tooth Abscess Treatment
Your endodontist will focus on treating the infection that caused the tooth abscess. They can diagnose the issue with an X-ray, which helps them see how far the infection has spread. Treatments for tooth abscesses may include draining the abscess, performing a root canal or extracting the infected tooth. You may need to take antibiotics to heal the infection and prevent it from spreading.
An experienced endodontist will discuss all your options with you and help you determine the best course of treatment. If you suspect you have a tooth abscess, contact Midtown Endodontist NYC today to book an appointment. Call us today at (646) 374-2569.
About Dr. Steven Lipner
Dr. Steven Lipner is a Root Canal Specialist stationed in NYC. He is highly experienced and provides excellent care at LipnerEndo, his Midtown East Manhattan practice. Dr. Lipner utilizes the most innovative dental technology, including Digital X-rays and the High-Powered Microscope. He strives for meticulous precision to give his patients the best possible results.
 Our Providers
Our Providers
 Blog
Blog
 Contact us
Contact us
 Endodontics
Endodontics
 Root Canal Treatment
Root Canal Treatment
 Emergency Root Canal
Emergency Root Canal
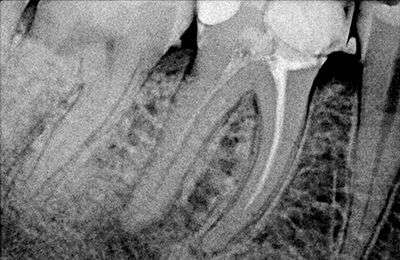 Root Canal Retreatment
Root Canal Retreatment
 Complimentary Teeth Whitening
Complimentary Teeth Whitening
 Teeth Whitening
Teeth Whitening





